Test setup
A variety of treatment delivery errors were introduced into 4 clinical H&N VMAT plans.
These plans were applied through the IQM onto a PTW Octavius 729 (local Gamma pass rate: 2%/2mm).
Which of the two systems will be able to detect the errors introduced into the VMAT delivery?
Test method
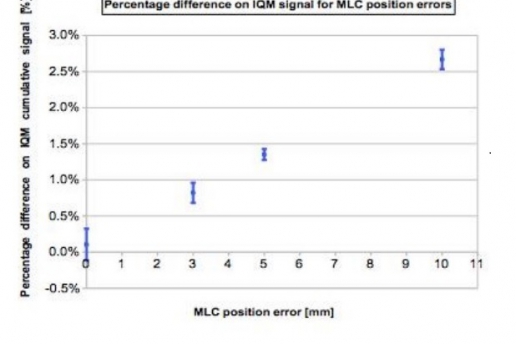
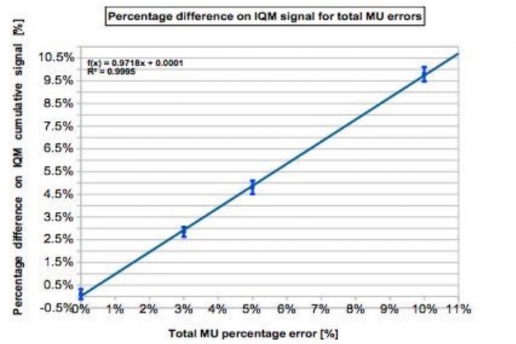
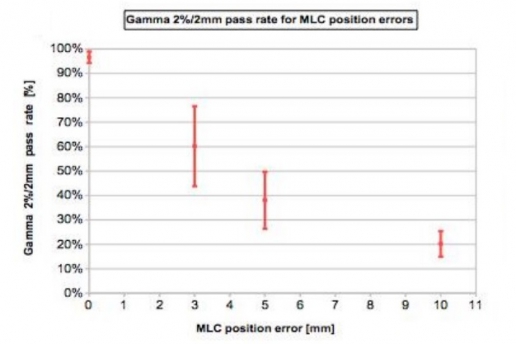
The errors introduced into the 4 H&N VMAT plans were 3, 5 and 10 % errors on total delivered MUs and with 3, 5 and 10 mm MLCs shift errors.
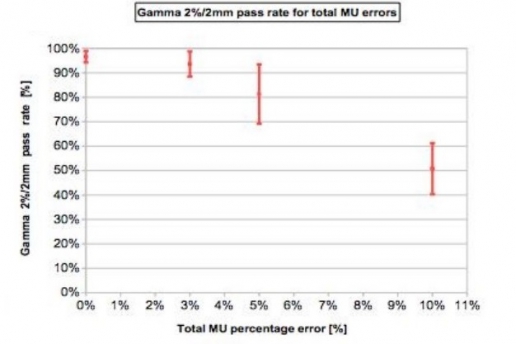
The cumulative IQM checksum value was measured and the percentage difference was calculated with respect to the non-modified plan. At the same time dose distribution maps were obtained through the PTW 2D array inserted in a rotating QA phantom (RT-smartIMRT, dose.point GmbH). The local gamma pass rates (2%/2 mm) were compared to the original plan values.
Test results
Both methods detect specifically MLC shift errors, while MU variations were better identified by IQM.
IQM shows a linear response with dose (R2=0.9995), while gamma analysis (as used by PTW Octavius) seems to have difficulty in identifying 3% and 5% MU variations.
Conclusion
IQM shows appreciable features in detecting real-time errors and promises considerable time-saving for QA measurements.
This test report is based on a publication created by Azienda Provinciale per i Servizi Sanitari, Trento (Italy).
Please click on the „Download“ button to download the complete publication.